

These microbes ferment food in the small intestine which produces hydrogen and other gases. When these mechanisms break down, unusually large numbers of microbes grow in the small intestine and this condition is known as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. The acidity of chyme when it enters the small intestine.Antimicrobial peptides and immunoglobulin secreted by small intestinal epithelial cells.Contraction of the smooth muscle in the lining wall of the gut, which moves the contents along the gastrointestinal tract to the large intestine.Various mechanism help to balance low microbial number in a healthy small intestine are: It is a primary site for the absorption of nutrients in humans and has a thinner mucus layer to help the absorption of nutrients. On the other hand, the small intestine relatively has a little number of microbes. To keep these microbes away from the gut wall, the epithelium secretes a thick layer of mucus. These microbes help in digestion, produce signaling molecules, stimulate the immune system, and synthesize vitamins.
Trillions of microbes are home to a healthy large intestine, it is known as gut microbiota these are very important to human health. Introduction of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth

We have discussed various important points of the SIBO which include Ayurvedic aspects, causes, and symptoms, risk factors with effective herbal and home remedies. This disease occurs in a small number of patients.
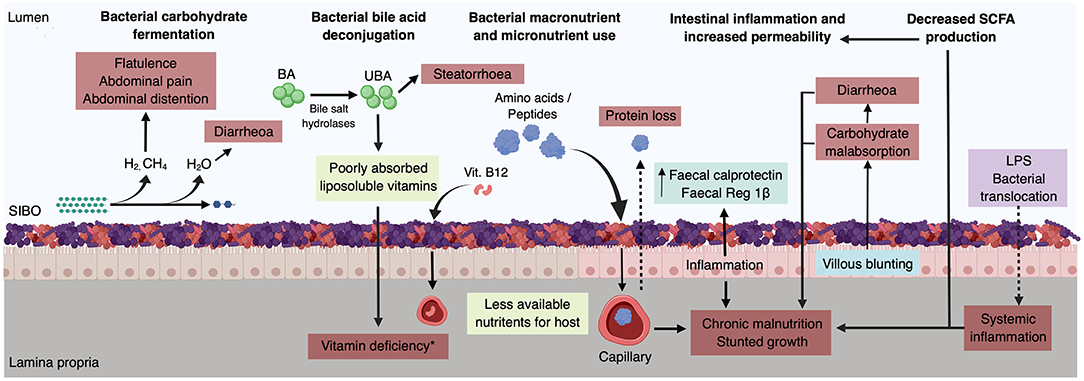
SIBO patients are suffering from diarrhea, weight loss, or malabsorption. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) defined as excessive bacterial growth in the small intestine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
